
from The Universe Explained
by Colin A. Ronan published by Henry Holt 1994
THE NATURE OF MATTER
PHYSICS
MYSTERIES
EXPLAINED
PHOTONS
CHAPTER
8
Section 1 E=mc2 Mass-Energy and Matter
Section 2 E x B Electromagnetic Propagation
Section 3 E=hv Unit Photons
MASS-ENERGY AND
MATTER
Section 1
The deduction of the Unit
Particle Substructure Theory of Standard Model particles allowed for the explanation
of the famous equation E=mc2 which states that mass
and energy are interchangeable quantities because the theory delineated the difference
between energy quanta and units of matter as components in structures of Standard
Model particles.
The equation does not state that matter and energy are interchangeable quantities,
only that combinations of mass-energy are interchangeable.
Mass-energy and matter are two distinctly different entities quantities.
Mass-energy is permanent in nature. The Unit
Particle Substructure Theory of Standard Model particles predicts that unit particles
of matter are permanent in nature also.
The Unit Particle Substructure Theory
of Standard Model particles predicts that energy must be required to be bound to
a unit particle of matter at all times.
The Unit Particle Substructure Theory
of Standard Model particles deduces that mass-energy bound in a particle as structural
energy is rest mass.
Mass-energy bound to a doublet substructure as momentum energy or kinetic energy
does not cause the substructure to have rest-mass, just momentum.
Photons have no rest mass because photons have doublet substructures, and doublet
substructures have no structural energy in the double particle substructure.
Particles of matter with a rest mass have energy bound in a closed loop as part of
the particle structure. Particles are composed of two components, unit charge unit
particles of matter and units of mass-energy.
Energy is what causes mass, not unit particles of matter.
Momentum energy is the energy causing the physical motion of a particle.
ELECTROMAGNETIC
PROPAGATION
Section 2
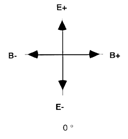
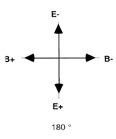
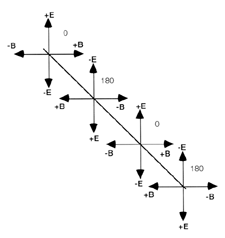
Photons of light are quanta of mass-energy that propagate through
spacetime using alternating electromagnetic fields.

UNIT
PHOTONS
Section 3
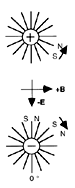
It is proposed that the photon is composed of a doublet substructure with a positive
unit of matter and an negative unit of matter, and some number of pairs of energy
units.
A unit photon is defined as composed of 2 quanta of energy bound to
two units of matter in a doublet substructure.
Planck's Law E=hv indicates that there is h (h bar) energy per cycle
or wave.
The quantity h is the amount of energy in one cycle of the two units
of energy in rotation about the two units of matter in a doublet in a unit photon.
The frequency value in Planck's Equation is proposed to represent the number of unit
photons bound on the doublet substructure of the photon. Each unit photon is pair
of energy units and accounts for one cycle of energy (frequency).
Title
Page of the
NATURE OF MATTER
Table of Contents of the NATURE OF
MATTER
The Background of Matter Home Page
Think you understand the Unit Matter
Substructure Theory?
Think you understand the Background of Matter Theory?
Comments welcome: jrees@starlight-pub.com
Last Update April 22, 2000
Copyright © 2000 Starlight Publishing Company Hermosa Beach, CA