
PART I
CHAPTER 3
STEP 3
Bottom of Step 3: Doublet Substructures of Unit Particles
Top of Step 3: Massless Doublet Substructures of Unit Particles

There were four steps of deduction followed in deducing the existence of the universal background of matter.
Question: How could Doublets Possibly Exist?
Answer: Unit Particles of Matter must not be Destructible
Non-Destructive Annihilation Hypothesi
The Alignments of Magentic Dipoles in Electron-Positron Annihilations
The Permanent Nature of Matter
QUESTION: HOW COULD DOUBLETS POSSIBLY EXIST?

How could a doublet substructure particle possibly exist without the two oppositely charged unit particles of matter in the doublet substructure self-annihilating?
ANSWER: THE UNIT PARTICLES OF MATTER MUST NOT BE DESTRUCTIBLE
Suppose then, that because a doublet substructure allows a
structural explanation for a magnetic dipole on a neutral neutrino, and because a
doublet substructure allows a structural explanation for unidirectional the helicity
of the neutrino, that the neutrino actually has a doublet substructure and that the
doublet consists of two oppositely charged, unit particles of matter.
The Non-Destructive Annihilation Hypothesis
The supposition that a doublet substructure exists,
which is composed of a positive charge unit particle of matter and a negative charge
unit particle of matter, leads one to suppose that a mechanism must exist which prevents
the two opposite charge unit particles of matter within the doublet substructure
from being destroyed.
Since the doublet substructure explains the magnetic dipole of the neutral neutrino
and the helicity of the neutrino, one must consider the possibility that a doublet
substructure exists in the neutrino. If a doublet substructure exists in the neutrino,
then the unit particles of matter must be non-destructible within the doublet substructure.
|
THE NON-DESTRUCTIVE ANNIHILATION HYPOTHESIS Unit particles of matter are neither created nor destroyed. |
A doublet substructure composed of two opposite charge unit
particles of matter forces a non-destructive annihilation hypothesis.
If a positive charge unit particle of matter and a negative unit particle of matter
come into equilibrium in the force of attraction between them, which must happen
in a doublet, then matter must not annihilate destructively.
Suppose that in the annihilation of an electron and a positron that the structural
unit particles of matter are not destroyed in the annihilation, rather suppose that
the energy is squeezed out of the electrical fields of the unit particles of matter
and that the unit particles still exist after the annihilation.
The Alignment of Magnetic Dipoles in Positron-Electron Annihilations
In the process of an electron-positron annihilation, the electron and positron form an atom of positronium, which is the electron and positron in revolution about a common center.

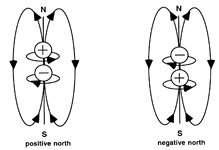
The positive north alignment has a positive unit
particle of matter at the northern most end of the common magnetic dipole. The negative
north alignment has a negative unit particle of matter at the northern most
end of the common magnetic dipole.
In a effort to mentally construct a doublet substructure which consists of two units
of matter, and using the collapse of the positronium in electron-positron annihilations
as a guide, consider the electrical fields of the electron and the positron during
the process of mutual annihilation.

As the electron and the positron approach each other in annihilation, the lines of force of the electrical fields are deformed toward the oppositely charged unit particle of matter by the force of electrical attraction.

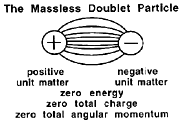
Suppose that when all of the electrical fields lines between the two units of matter
are neutralized, that the two particles reach a point of equilibrium in their mutual
attraction.
For a doublet substructure to exist, there must be some mechanism that keeps the
positive and negative units from ultimately destroying one another. Whatever the
process or mechanism that stops the actual destruction is need not be known because
the fact is something keeps the units of matter from being destroyed in the doublet
substructure.
THE PERMANENT NATURE OF MATTER
The existence of a massless doublet substructure forces the non-destructive annihilation
hypothesis to be postulated.

Massless Doublets
The non-destructive annihilation hypothesis declares that units
of matter are permanent in nature, like units of energy, and like energy, are neither
created nor destroyed.
The doublet substructure is massless meaning it has no rest mass, or equivalently,
no structural energy.

The existence of a doublet substructure causes the non-destructive annihilation hypothesis to be postulated. The non-destructive annihilation hypothesis postulates that matter is permanent in nature, as energy is known to be.

Massless Doublets
Doublet substructures demand that matter, which is composed
of units of matter, be permanent in nature.
Title
Page of the
Nature of Matter
Table of Contents of the Nature of Matter
Comments welcome: jrees@starlight-publishing.com
Last Update: October 7 2000
Copyright © 2000
Starlight Publishing Company
Hermosa Beach, CA