Lambda
CHAPTER 2 PARTICLE COMPOUNDS
Section 1 Hadrons
Section 2 Bosons
Section 3 Hyperons
Section 4 Mouns
Section 5 Intermediate Vector Bosons
LAMBDA 3.1
Lambda is a complex compound composed of a first order charged pion bound to proton through a particle bond.
![]()
![]()
Lambda
The host of the weak bond is not clear. Since the host particle of the weak bond
is not clear, it is not clear whether the decay products are dependent on which sub-unit
is the host of the weak bond. The convention here will be to consider the proton
as the non-weakly bound sub-unit when possible.
The particles of the weak force electrical bond make the particle bond possible.
The assumption is made that the weak force bond constituents, the negative unit particle
of matter and the neutrino, can bond to either the pion or the proton during the
decay process. Therefore, the decay products are either a pi- and a proton, or, a
pi0 and a neutron.
Positive Sigma is a complex compound composed of a second order neutral pion bound to a proton by at least one particle bond.
![]()
![]()
Positive Sigma
In positive sigma, the weak force bound negative unit particle of matter can attach to either the pi+ or the proton during decay. Therefore, the resultant decay products are either a pi+ and a neutron, or a second order neutral pion and a proton.
SIGMA
Neutral Sigma is a compound of a second order neutral pion bound to a neutron by at least one particle bond.
![]()
![]()
Neutral Sigma
One decay mode of neutral sigma is when the neutron and the second order neutral
pion split. Alternatively, a pair of weak force bonded unit particle of matters could
collapse producing a lambda particle and neutrinos.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
pi0 and a neutron
or lambda + neutrino(s)
Neutral Sigma Decay Products
Negative Sigma is a complex compound composed of a negatively charged pion bound to a neutron by a particle bond.
![]()
![]()
Negative Sigma
For negative sigma, both of the weakly bound negative unit particle of matters may not bind to the same sub-unit during decay. Therefore, the major decay products are a pi- and a neutron.
![]()
![]()
![]()
XI
Neutral Xi is a compound composed of one first order negative pion and one second order neutral pion bound to a proton by two particle bonds.
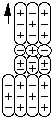
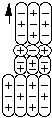
Neutral Xi
The principal decay mode of the neutral Xi particle is to decay into a lambda and a second order neutral pion.
Negative Xi is a complex compound composed of two first order negative pions bound to a proton by particle bonds. Anti-Negative Xi is centered around the negative anti-proton which has two positive pions bound to it.
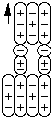
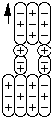
Negative Xi
The principal decay mode of Xi- is to divide into a lambda and a negative pion.
The greater mass of negative Xi over the mass of neutral Xi, even though neutral Xi contains more unit particle of matters, is explained by neutral Xi having only one unpaired weakly bound unit particle of matter and negative Xi having two unpaired weakly bound unit particle of matters which have the same charge.
OMEGA
Omega Minus is a compound composed of two first order negative pions,
a second order neutral pion, and a proton, all bound together by particle bonds.
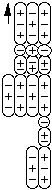
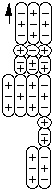
Omega Minus
Omega- is basically a neutral Xi with an additional negative pion bound to it.
What is not clear is whether the negative pion is attached to the proton or to the
neutral pion.
Omega- has two principal decay modes. Not surprisingly, one principal decay mode
is when omega- splits into a neutral Xi and a negative pion. The other principal
decay mode is when omega- splits into a Xi- and neutral pion.
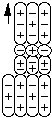
![]()
![]()
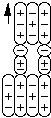
![]()
![]()
Xi0 + pi- or Xi- + pi0'
Omega Minus Decay Products
Think you understand the Unit Matter Substructure
Theory? Take
the quiz!
Comments: jrees@starlight-pub.com
Last Update May 23, 2000
Copyright © 2000 Starlight
Publishing Company Hermosa Beach, CA