
THE NATURE OF
MATTER
by James Rees
THE UNIT ELECTRICAL MATTER SUBSTRUCTURE THEORY

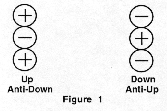
In the illustrations above:
- positive and negative units of matter are represented by the circles with the positive and negative signs
- bound structural units of energy are represented by the elliptical loops with arrows indicating the direction of rotation
(energy rotation is quantum angular momentum; the motion of the energy is described by the quantum mechanical wave function)
- 'N' indicates the north end of the magnetic dipole of the unit matter substructure.
The deduction of units of matter as components of Standard Model fundamental particles means there two fundamental components which compose everything else;
units of energy and units of matter.
Units of matter have unit electrical charge, either positive or negative,
because the unit particles of matter are the fundamental units of electrical charge.
Units of matter are themselves only centers of electrical charge, and do not themselves
posses mass nor energy. The units of matter host bound energy, but are not made of
energy, just electrical charge.
The two types of units of matter, positive and negative, are the fundamental units
of electrical charge.

Energy is a separate and distinct component of Standard Model particles apart from electrical charge. The rest mass of a particle is the structural energy which is bound to the particle's unit matter substructure.
In the first step of deduction, up
and down quarks were deduced to have a triplet unit charge, unit matter substructure
from this evidence:
(short explanations below on this page)
The math of quark fractional charge
The tripolar charge of the strong force
The SU(3) symmetry of the strong force
The deduction of the triplet unit charge substructures of quarks
elucidated the distinction between energy quanta and unit charge, unit particles
of matter as structural components of Standard Model fundamental particles.
The distinction between units of energy and units of matter as structural
components of Standard Model particles allowed for the subsequent deduction of doublet
substructures.
In the second step of deduction, neutrinos
were deduced to have a doublet unit charge, unit particle of matter substructure
from this evidence:
(short explanations below on this page)
There are only two neutrinos in each family.
Neutrino Unidirectional Spin
Neutron Magnetic Dipole
Weak Force Parity Violation
SU(2) Symmetry of the Weak Force
Ultimately, photons were deduced to be doublet substructures with two counter rotating
sets of bound energy.
The Math of Quark Fractional Charge
The Tripolar Charge of the Strong Force
The SU(3) Symmetry of the Strong Force
The Math of Quark Fractional Charge
The first step of deduction deduced the Quark Partial Group Mathematics which
is manifested by the triplet unit particle of matter substructure forming up and
down quarks.
The same two symmetric triplets which account for the up amd down quarks, also account
for the anti-up and anti-down quarks.
The fractional electrical charge mathematics of the up and
down quarks, as well as the anti-up and anti-down quarks, are all explained with
just the two symmetrical triplets. The two triplets are also the only two triplets
possible for a group of three units with each unit one of two possible types.
Quark fractional charge is group ratio mathematics for a group of three unit charge
particles with one of the two types of units of matter, positive or negative, being
counted in the numerator over the total group in the denominator.
For instance, in normal matter quarks, it is positive units that are tracked in the numerator over the group total in the denominator. The up triplet has two positive units out of a total group of three. The group has a group charge of +1. Multiplying group charge by the ratio of the chosen unit gives +1 * 2/3 = +2/3. The down triplet has one positive unit over a group of three with a group charge of -1, therefore -1 * 1/3 = -1/3.
The quark fractional charge mathematics is partial group mathematics where one type of unit, positive or negative, is tracked in the numerator with the denominator being the total group.
|
Normal Matter |
Anti-Matter |
|||
|
Positive Matter |
Negative Matter |
Negative Matter |
Positive Matter |
|
|
up = +2/3 |
up = +1/3 |
anti-up = -2/3 |
anti-up = -1/3 |
|
|
down = -1/3 |
down = -2/3 |
anti-down = +1/3 |
anti-down = +2/3 |
|
The quark fractional charge mathematics is partial group mathematics where one type of unit, positive or negative, is tracked in the numerator with the denominator being the total group.
For instance, in normal matter quarks, it is positive units that are tracked in the numerator over the group total in the denominator. The up triplet has two positive units out of a total group of three. The group has a group charge of +1. Multiplying group charge by the ratio of the chosen unit gives +1 * 2/3 = +2/3. The down triplet has one positive unit over a group of three with a group charge of -1, therefore -1 * 1/3 = -1/3.
The left hand columns of Table 1 and Table 2
are the partial group ratios used in known physics. The right hand columns of Table
1 and Table 2 are partial group ratios that were not known until the deduction
of the unit matter substructures. For normal matter, there are not yet widely known
negative matter ratios, and for anti-matter there are not widely known positive matter
ratios.
SU(3) Symmetry and the Tripolar Charge of the Strong Force
The quark triplet unit matter substructure not only offers a physical mechanism
to explain the quandry of fractional charge existing on a supposed fundamental particle,
it also offers a physical mechanism to explain the tripolar color charge of the strong force
and the associated SU(3)
symmetry of the strong force observed in energetic
interactions between quarks.
The reason energy exchanged between quarks manifests a tripolor charge and exhibits
SU(3) symmetry is because the structural energy of a quark is divided among three
axes on three units of matter.
SU(3) is special unitary symmetry with three axes of rotation which equates physically
to a constant amount of energy bound to three interacting axes of rotation on three
units of matter in the quark triplet substructure.
Neutrino Doublet Unit
Matter Substructures
Full STEP 2 Explanation
The neutrino doublet substructure is manifested by these
phenomena:
Neutrino Unidirectional Spin
There are only two neutrinos in each family.
Neutron Magnetic Dipole
Weak Force Parity Violation
SU(2) Symmetry of the Weak Force

The unidirectional spin of neutrinos is caused by two things,
the weak force bond and by the doublet substructure of the neutrino. Energy binds
to matter in a specific direction depending on the charge of the unit of matter,
right hand binding for positive units and left hand binding for negative units of
matter. The weak force deposits momentum energy onto the doublet substructure creating
the neutrino with the energy binding in the appropriate direction.
For example, anti-neutrinos have right hand quantum angular momentum which is energy
bound with right hand rotation to the right hand positive unit of matter in the doublet
substructure.
Neutron substructure and weak force parity violation are discussed further in the
next section.
SU(2) is special unitary symmetry with two axes of rotation which equates physically
to a constant amount of energy bound to two interacting axes of rotation on the two
units of matter within the doublet substructure.
The doublet unit particle of matter substructure was deduced
to have no internal structural energy in the particle substructure, which equates
to no rest mass. Neutrinos were deduced in STEP 2 to be massless doublet
substructures with momentum energy bound in one direction of rotation.
Neutron Substructure and the Weak Force
The doublet substructure of the neutrino offers a direct
mechanism to explain the weak force parity violation of neutron decay, which in turn
explains the unidrectional spin of the neutrino.
The weak force parity violation of neutron decay was deduced to be caused by the
unit matter substructure of the neutron and the need for the unit particles of matter
within the neutron substructure to be magnetically aligned.
The unidirectional helicity of neutrino spin is ultimately caused by energy only
being able to bind to a unit of matter in one direction depending on the charge of
the unit of matter, while the doublet substructure of the neutrino is manifested
because energy can bind in right rotation only and because of the SU(2) symmetry
of the weak force.
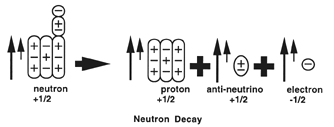
The little arrow indicates north on the magnetic
dipole.
The large arrow indicates direction of momentum.
The anti-neutrino and the electron emerge from neutron decay
with the electron exhibiting left hand spin and the anti-neutrino exhibiting right
hand spin because the unit particles of matter within the neutron substructure are
magnetically aligned and the unit particle of matter that formed the electron in
the decay was bound in the neutron unit matter substructure in such a way as to emerge
heading north on its magnetic dipole as an electron.
Photon Doublet Unit
Matter Substructures
Full Chapter 8 Photons Explanation
Photons manifest a doublet unit particle of matter substructure.
The correlation of the magnetic and electrical fields of electromagnetic propagation
within photons with how the magnetic and electrical fields would propagate if two
oppositely charged counter-rotating energies were hosted by the two unit particles
of matter in a doublet substructure revealed an exact match. The electromagnetic
propagation of photons is explainable with two sets of counter-rotating momentum
energy (spin 1) in rotation about each of two unit particles in a doublet substructure.
The energy rotation loops are only symbolic of bound energy rotation. Energy rotation is described by the wave function. Part III Chapter 9 The Rotation of Energy
Photons have two sets of bound energy, one set hosted by the positive unit particle of matter which creates the positive electric field, and one set of energy hosted by the negative unit particle of matter which creates the negative electric field. The electrical fields in the photon change poles twice per energy rotation due to the counter rotating motion of the energy hosted by the two unit particles in the doublet.

Doublets
Standard Model Particle Compounds - Protons,
Neutrons, Pions
The neutron is a proton with a weak force bound negative unit of matter bound through
a doublet. The weak force bond is represented by a doublet connecting a single unit
to a triplet within the host nucleus particle.
![]()
![]()
![]()
Proton
![]()
![]()
![]()
ud
pion
- rest mass is internal structural energy bound to the particle's unit matter substructure
- doublet substructures have no internal structural energy (no rest mass)
- neutrinos are doublet substructures with one set of momentum energy
- photons are doublet substructures with two sets of momentum energy
- there must exist many doublet substructures which have no momentum energy
- bosons have an even number of units of matter in their substructure
- fermions have an odd number of units of matter in their substructure
- strong force SU(3) symmetry is caused by the triplet substructure of quarks
- weak force SU(2) symmetry is caused by the doublet substructure of neutrinos
- wave-particle duality is caused by the two structural components - energy and matter
The Chart of Explanations has links to explanations of present mysteries of physics.
There were four steps of deduction followed in deducing of the existence of the universal
background of matter. The first two steps of deduction deduce the unit matter substructure
of Standard Model particles.

The Four Steps of Deduction
The last two steps of deduction deduce the existence of a universal background ocean composed of particles of pure matter.
Summary of the Steps of Deduction
Chapter 1 The Background of Matter
Chapter 3 The Steps of Deduction
Chapter 4 Evidence of a Background of Matter
PART III PHYSICS MYSTERIES EXPLAINED
CHART OF Physics MYSTERIES EXPLAINED
Title Page of the Nature of Matter
Table of Contents of the Nature of Matter
Comments welcome: jrees@starlight-publishing.com
Last Update: 01/11/01
Copyright © 2001
Starlight Publishing Company
Hermosa Beach, CA